
Health Safety & Environment Management System (HSEMS)
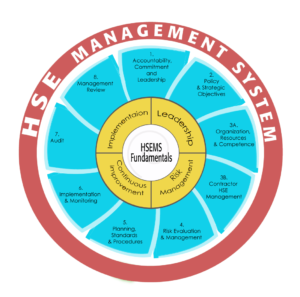 Health, Safety and Environment (HSE) is an umbrella term for the laws, rules, guidance and processes designed to help protect employees, the public and the environment from harm. In the workplace, the responsibilities for designing and implementing appropriate procedures is often assigned to a specific department, often called the “HSE” department which is responsible for environmental protection, occupational health and safety at work. HSE management has two general objectives: prevention of incidents or accidents that might result from abnormal operating conditions and reduction of adverse effects that result from normal operating conditions.
Health, Safety and Environment (HSE) is an umbrella term for the laws, rules, guidance and processes designed to help protect employees, the public and the environment from harm. In the workplace, the responsibilities for designing and implementing appropriate procedures is often assigned to a specific department, often called the “HSE” department which is responsible for environmental protection, occupational health and safety at work. HSE management has two general objectives: prevention of incidents or accidents that might result from abnormal operating conditions and reduction of adverse effects that result from normal operating conditions.
Regulatory requirements play an important role in the role and HSE managers must identify and understand relevant HSE regulations, the implications of which must be communicated to executive management so the company can implement suitable measures. Organisations based in the United States are subject to EHS regulations in the Code of Federal Regulations, particularly CFR 29, 40, and 49. Still, EHS management is not limited to legal compliance and companies should be encouraged to do more than is required by law, if appropriate.
From a health & safety standpoint, it involves creating organized efforts and procedures for identifying workplace hazards and reducing accidents and exposure to harmful situations and substances. It also includes training of personnel in accident prevention, accident response, emergency preparedness, and use of protective clothing and equipment.
From an environmental standpoint, it involves creating a systematic approach to complying with environmental regulations, such as managing waste or air emissions all the way to helping site’s reduce the company’s carbon footprint.
Successful HSE programs also include measures to address ergonomics, air quality, and other aspects of workplace safety that could affect the health and well-being of employees and the overall community.
Contents
- 1Other names
- 2Regulatory Agencies
- 3General categories
- 4Specific Categories
- 5History
- 6Example
- 7See also
- 8External links
- 9References
Other names
HSE goes by a number of acronyms which may exclude environment or include security and quality.
| Acronym | Name | Group |
| OHS | Occupational Health and Safety | Occupational Health and Safety |
| HSE | Health, Safety and Environment | Health, Safety and Environment |
| EHS / EH&S | Environment, Health and Safety | |
| SHE | Safety, Health and Environment | |
| QHSE | Quality, Health, Safety, and Environment | Quality, Health, Safety, and Environment |
| HSEQ | Health, Safety, Environment and Quality | |
| HSSE | Health, Safety, Security and Environment | Health, Safety, Security and Environment |
| QHSSE | Quality, Health, Safety, Security, and Environment | Quality, Health, Safety, Security, and Environment |
| HSSEQ | Quality, Health, Safety, Security, and Environment |
Regulatory Agencies
See also: Occupational safety and health – National legislation and public organizations
United States
- Federal / International
- Occupational Safety & Health Administration (OSHA)
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
- Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC)
- Mining Safety & Health Administration (MSHA), etc.
- European Union (EU Standards) –Health & Safety At Work Act
- State
- Safety & Health Council of North Carolina, Massachusetts Nuclear Regulatory Commission, etc.
- Local
- Fire Department, Building Code Inspections
General Categories
EHS guidelines cover categories specific to each industry as wells as those that are general to most industry sectors. Examples of general categories and subcategories are:
| 1. Environmental | |
| 1.1 Air Emissions and Ambient Air Quality
1.2 Energy Conservation 1.3 Wastewater and Ambient Water Quality 1.4 Water Conservation 1.5 Hazardous Materials Management 1.6 Waste Management 1.7 Noise 1.8 Contaminated Land |
|
| 2. Occupational Health and Safety | |
| 2.1 General Facility Design and Operation
2.2 Communication and Training 2.3 Physical Hazards 2.4 Chemical Hazards 2.5 Biological Hazards 2.6 Radiological Hazards 2.7 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) 2.8 Special Hazard Environments 2.9 Monitoring |
|
| 3. Community Health and Safety | |
| 3.1 Water Quality and Availability
3.2 Structural Safety of Project Infrastructure 3.3 Life and Fire Safety (L&FS) 3.4 Traffic Safety 3.5 Transport of Hazardous Materials 3.6 Disease Prevention 3.7 Emergency Preparedness and Response |
|
| 4. Construction and Decommissioning | |
| 4.1 Environment
4.2 Occupational Health and Safety 4.3 Community Health and Safety |
|
Specific Categories
See also: Occupational safety and health -By industry
History
The chemical industry introduced the first formal EHS management approach in 1985 as a reaction to several catastrophic accidents (like the Seveso disaster of July 1976 and the Bhopal disaster of December 1984). This worldwide voluntary initiative, called “Responsible Care“, started by the Chemistry Industry Association of Canada (formerly the Canadian Chemical Producers’ Association – CCPA), operates in about 50 countries, with central coordination provided by the International Council of Chemical Associations(ICCA). It involves eight fundamental features which ensure plant and product safety, occupational health and environmental protection, but which also try to demonstrate byimage-building campaigns that the chemical industry acts in a responsible manner. Still, this initiative is restricted to the chemical industry.
Since the 1990s, general approaches to EHS management that may fit any type of organisation have appeared in international standards such as:
- ISO 14001for environmental management
- OHSAS 18001for occupational health and safety management, first published in 1999
- theEco-Management and Audit Scheme (EMAS), developed by the European Commission in 1993
In 1998 the International Finance Corporation established EHS guidelines.
Example
As a typical example, the activities of a Health, Safety and Environment (HSE) working group might focus on:
- exchange of know-how regarding health-, safety- and environmental aspects of a material
- promotion of good working practices, such as post-use material collection for recycling
See also
- Occupational safety and health
- Robert W. Campbell Award, an Award for Business Excellence through EHS Management.
- Safety engineering
External Links
- NAEM, the premier Association for EHS Management: What is EHS?
- International Finance Corporation: World Bank Group Environmental, Health, and Safety Guidelines
- International Network for Environmental Management
HSEMS TEMPLETS
The most recent version of the Safety Program Development course provides students with a number of editable templates for various components in a heath and safety management system.
These are freely available for your company to use, edit, and adapt for your specific management system needs.
The templates have been grouped into bundles based on chapters within the Safety Program Development course. Templates are in MS-Word or MS-Excel format while examples of how to use the templates are provided in PDF format.
Chapter 2 – Management Involvement and Committment
enform-spd-chapter-2-templates- HSE Annual Goals
- Accountability Monitoring System
- Safety Performance Review
- Discipline Action Reporting Form
- Quarterly Executive Tour
Chapter 3 – Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment and Control Measures
enform-spd-chapter-3-templates- Facility Inspection
Chapter 4 – Managing Hazards in the Workplace
enform-spd-chapter-4-templates- Position/Discipline Inventory
- Position Inventory and Task List
- Formal Hazard Assessment
- Site Specific Assessment
- Action Card
- Hazard Report Form
- Workplace Inspection-Extended
- Equipment Maintenance Log
- Vehicle Maintenance Log
- Hazardous Materials Log
Chapter 5 – Training
enform-spd-chapter-5-templates- Safety Training Requirements Matrix
- Employee Orientation
- Site-Specific Orientation
- On-the-Job Training Record
- Training Record Log
- Competency Checklist
Chapter 6 – Emergency Response Planning
enform-spd-chapter-6-templates- ERP Resource Assessment
- Emergency Drill Record
- Emergency Drill Evaluation
Chapter 7 – Incident Reporting and Investigation
enform-spd-chapter-7-templates- Action Card
- Action Card Report Summary
- Incident Investigation Report Form
Chapter 8 – Corporate Communication
enform-spd-chapter-8-templates- Safety Meeting Report Form
- Record of Journey Form
- Audit Action Plan
